3.PHYSIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF RICE BRAN ARABINOXYLAN DERIVATIVE (Biobran)
3.1 Immuno Regulation
(a) Enhancement of human NK cell activity by modified arabinoxylan from Rice Bran
(Biobran MGN-3)
1. In vitro test
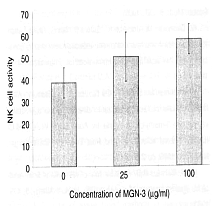
Rat-derived NK cells were incubated with K-562 tumor cells, which were the target
cells, in the presence of Biobran MGN-3, and the amount of the K-562 cells dissolved
was measured by 51Cr-release assay. The dissolved amount increased
concentration-dependently between Biobran MGN-3 concentrations of 25 μg/ml and 100
μg/ml, which confirmed that the increase of NK activity was due to Biobran MGN-3.
2. In vivo test (rat)
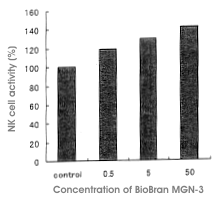
Biobran MGN-3 was given orally to Sprague-Dawly rats and after two weeks the change
of NK cell activity was measured. Rats were divided into three groups with doses of
0.5 mg, 5 mg and 50 mg/kg/day, with five rats per group. NK cell activities
increased dose-dependently with the administration of Biobran MGN-3. Compared with
the control group, the activities increased by 119%, 130% and 142% for the 0.5 mg, 5
mg and 50 mg dose groups, respectively. In the 50 mg dose group, the activity
increased by 132% compared with the control group within three days of the dose
initiation. The increase of NK cell activities by Biobran MGN-3 could be attributed
to the increased dissolving power of NK cells but also depended on the number of NK
cells. Some difference in effect was observed between male and female rats, and the
manifestation of the effect was more remarkable in female rats (Figure 3).
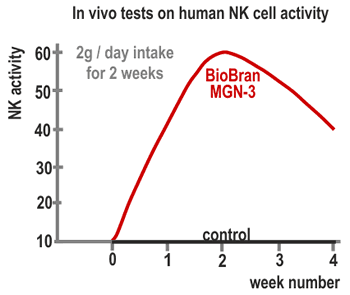
3. Actions on humans
A 60-day continuous intake test of Biobran MGN-3 was conducted on 24 healthy
subjects (15 women and 9 men, average 34 years old) and the change in NK cell
activities was observed. The subjects were divided into three groups with intake
amounts of 15 mg/kg/day, 30 mg/kg/day and 45 mg/kg/day, with 8 subjects per group.
Twenty cc of blood was collected from each participant: prior to the intake of
Biobran MGN-3, after one week, after one month, after two months (at the termination
of the test) and one month after the termination and NK activities were measured. In
the 30 mg and 45 mg intake groups, NK activities increased approximately two-fold
one week after initiation of intake and reached three-fold in two months. In the 15
mg intake group, the activity rapidly increased from one month after initiation and
reached almost the same level as in the 30 mg and 45 mg groups in two months. One
month after the termination of the intake NK activities returned to the level before
the intake (Figure 4). These results suggested that the intake of 15-45 mg/kg/day of
Biobran MGN-3 influences NK activities in human.
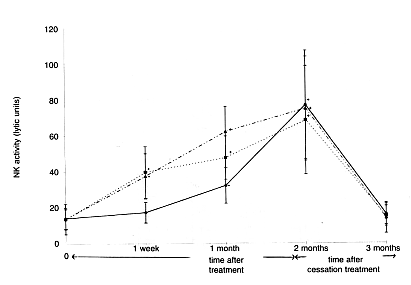
<Figure 4: Time and dosage dependence of natural killer (NK) cell
activation by Biobran MGN-3 against K562 tumour cells
…_.._.._.._ = 45mg/kg/day;
………… =30mg/kg/day;
_______ =15mg/kg/day
4. Mechanism of Biobran MGN-3 action on NK cells
Both in vitro and in vivo tests confirmed that the number of cytotoxic granules
increases in NK cells stimulated by Biobran MGN-3. The increase of binding ability
to target cells was also investigated. NK cells of a human who took 45 mg/kg/day of
Biobran MGN-3 for 30 days were incubated with K-562, which were the target cells,
and the increase of the binding ability was measured. After NK cells and K-562 tumor
cells were incubated at 4ºC for one hour, 200 NK cells were measured and the binding
rate with K-562 was calculated. The binding rate of NK cells to the target cells
(K-562) in a subject who took Biobran MGN-3 significantly increased to 38.5%
compared with 9.4% before intake (Figure 5). The typical photograph that indicates
binding is shown in Figure 6.
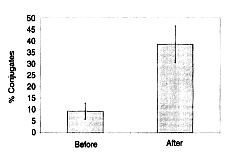 Figure 5: Percentage of conjugate formation between natural killer
(NK) cells and K562 target cells.
Figure 5: Percentage of conjugate formation between natural killer
(NK) cells and K562 target cells.
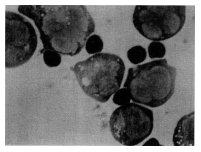 Figure 6: Natural killer (NK) effector-tumour targets conjugate
formation.
Figure 6: Natural killer (NK) effector-tumour targets conjugate
formation.
Ghoneum M. (Drew Univ., USA):INT. IMMUNO THERAPY XIV (2) PP.89-99, 1998
(b) In vitro effect of Biobran MGN-3 on macrophage group cell activity
The effect of Biobran MGN-3 on macrophage group cells in inducing the production of
pharmacological mediators has been investigated. TNF-a, IL-6 and NO were assayed as
mediators. Macrophage cells were incubated with various concentrations of Biobran
MGN-3 (1-100µg/ml) and supernatants were collected for assay of mediators. TNF-a was
assayed by cytotoxicity on L929, IL-6 by cytosis on B13.19 and NO colorimetrically
by reaction with Griess reagant. LPS was used as a positive control.
- Using Murine macrophage cell line RAW264.7, Biobran MGN-3 showed strong activity
on the three mediators at concentrations greater than 10µg/ml, as did LPS.
- Murine peritoneal macrophages(C3H/He). The effect of Biobran MGN-3 against the
macrophage originating from peritoneal cavity of normal mouse is showed in
Figure 7. Again Biobran MGN-3 showed strong activity at concentrations above
10µg/ml.
- Human macrophage cell line U937. Biobran MGN-3 induced strong activity as
measured by production of cytokines TNF-a and IL-6, equivalent to LPS at
100µg/ml.
The results show that Biobran MGN-3 is a potent substance for activating either
normal mouse or human macrophage. The studies suggested active concentrations of
over 10µg/ml.
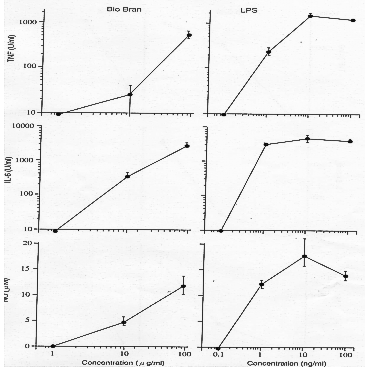 Figure 7: Murine peritoneal macrophages (C3H/He mice)
Matsuura M. (Jichi Medical School, JAPAN) : Report of Jichi Medical school
Figure 7: Murine peritoneal macrophages (C3H/He mice)
Matsuura M. (Jichi Medical School, JAPAN) : Report of Jichi Medical school
(c) Immunostimulation and cancer prevention
Several studies have established the excessive cancer risk for workers exposed to
various chemicals common in the workplace. A study was designed to examine the
immune alteration associated with exposure to toxic chemicals and the possibility of
counteracting chemical toxicity using Biobran MGN-3.
Eleven individuals who had been exposed to chemicals in the workplace participated
in the study. The participants demonstrated immune dysfunction as indicated by: low
levels of natural killer (NK) cell activity (10.2±4.2 LUs), lymphocyte blastogenic
responses to T-cell mitogens (PHA, 39060±12517cpm and COMA, 36224±11922cpm) and
B-cell mitogen (PWM, 16550±6330cpm), compared to control responses. Subjects
received Biobran MGN-3 at a dose of 15mg/kg/day for four months. Treatment with
Biobran MGN-3 increased NK cell activity 4 and 7 fold at two and four months
respectively, while T and B-cell functions were 130-150% higher than base line
values.
Ghoneum M. (Drew Univ., USA) : The abstract of the 7th International Congress on
Anti-Aging & Biomedical Technolgies Conference Proceedings Manual, 1999
(d) Production of TNF-α and IF-γ from Human PBL by Biobran MGN-3 Modified
Arabinoxylan from Rice Bran.
The mechanism by which Biobran MGN-3 elevates NK cytotoxic activity has been
investigated. This was done by testing the action of Biobran MGN-3 on the levels of
both tumor necrosis factor-α, (TNF-α) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) secretions and on the
expression of key cell surface receptors.
Peripheral blood lymphocytes were treated with Biobran MGN-3 at concentrations of
0.1 mg/ml and 1 mg/ml, and supernatants were subjected to enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay. Results showed that Biobran MGN-3 is a potent TNF-α inducer and
the effect was dose-dependent. Biobran MGN-3 concentration at 0.1mg/ml and 1 mg/ml
increased TNF-α production by 22.8- and 47.1-fold, respectively. Biobran MGN-3 also
increased production of IFN-γ but at lower levels as compared to TNF-α. With respect
to key cell surface receptors, Biobran MGN-3 increased the expression of CD69, an
early activation antigen at 16 hours after treatment. Furthermore, the interleukin-2
receptor CD25 and the adhesion molecule ICAM-1 (CD54) were up-regulated after
treatment with Biobran MGN-3. Treating highly purified NK cells with Biobran MGN-3
also resulted in increased levels of TNF-α and IFN-γ secretion in conjunction with
augmentation of NK cell cytotoxic function. Furthermore, addition of Biobran MGN-3
to interleukin-2-activated NK cells resulted in a synergistic induction of TNF-α and
IFN-γ secretion.
Ghoneum M. (Drew Univ., USA), Jewett A. (UCLA, USA) : Cancer Detection and Prevention
Vol.24/Issue 4, 2000
(e) The effect of modified rice-bran arabinoxylan on NK activity of human peripheral
blood lymphocytes.
The effects of Biobran MGN-3 and its molecular fractionates on NK activity have been
investigated High molecular weight fraction (M.W. 10-50 kDa) obtained by gel
filtration technique using Sephadex G-25 and G-75 was added to human peripheral
blood lymphocytes. After 3-days incubation, NK activity was determined.
Fluorescence-labeled K-562 cell line was used as the target cells and the activity
was determined gy fluorescence method using Tere Scan. The same experiment was
conducted in the presence of IL-2.
In these experiments no significant differences were found in the activation of NK
cells either by BioBan Biobran MGN-3 or by the high molecular weight fraction.
However, when IL-2 was added at the same time and incubated, increased NK activity
was observed compared to the addition of IL-2 by itself. This indicates that Biobran
MGN-3 activates NK cells in the presence of IL-2 and that such activity is also
present in the high molecular weight fraction.
Ueda Y., Shimomura C. (Chiba Univ., JAPAN) : The abstract of the 2002 Annual Meeting
of the Japan Society for Bioscience, Biotechnology and Agrochemistry
3.2. Anti-Viral Effect
Anti-HIV activity in Vitro of Biobran MGN-3
Anti-HIV activity of Biobran MGN-3 has been evaluated in vitro. First, the
inhibitory action against the production of the HIV-1 p24 antigen was evaluated.
Mononuclear cells collected from three healthy subjects were incubated with the
HIV-1 SF strain at 37ºC for one hour in the presence of Biobran MGN-3. The Biobran
MGN-3 concentrations were 0-100 μg/ml. Biobran MGN-3 concentration-dependently
inhibited the production of the HIV-1 p24 antigen (Figure 8).
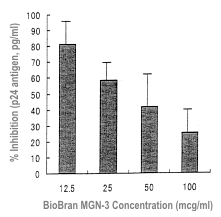
Next, the inhibitory action against syncytia formation was evaluated. Mononuclear
cells from five AIDS patients were incubated with PHA in the presence of Biobran
MGN-3 at 37ºC for seven days. Biobran MGN-3 concentrations were 0-100 μg/ml. Biobran
MGN-3 concentration-dependently inhibited syncytia formation, and the maximum
inhibitory rate was 75% with 100 μg/ml 7) (Table 1).
 |
|
Table 1
| Inhibition of Syncytia Formation by Biobran |
| Biobran dosage (μg/ml) |
Syncytia formation (SF) |
| No. of SF |
% Inhibition |
0
12.5
25
50
100
|
42.0±8
25.8±7
21.5±5
15.8±4
10.5±3
|
00.0
38.5
50.0
62.5
75.0
|
|
| Figure 8 |
|
|
Ghoneum M. (Drew Univ., USA):Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications
243, (1998)
3.3. Anti-Tumor Effect
(a) Study on the growth inhibiting component of cancerous cells in culture cell
lines derived from modified rice-bran arabinoxylan
In this study, the growth inhibiting effect of Biobran MGN-3 modified rice-bran
arabinoxylan on various cancerous cell lines such as HL60, K562, HLE was
investigated, and the potential differentiation-induction of HL60 and K562. Biobran
MGN-3 was added to the culture cell lines. After 3-days incubation, the rate of live
cells decreased in all cells lines as the amount of Biobran MGN-3 added increased.
After precipitation with ethanol, the precipitate was mixed with distilled water and
the supernatant was fractionated using Sephadex G-25 column. It was fractionated
into 3 fractions (A,B,C) which were added to the culture cell lines. Growth
inhibiting effects were observed with C fraction for HL60 and K562 and with B and C
fractions for HLE. In addition, from Giemsa stain and nonspecific esterase stain,
potential differentiation-induction was indicated for HL60 and K562. These results
indicate that Biobran MGN-3 has components which show growth inhibition of cancerous
cells and the potential differentiation-induction for HL60 and K562.
Masada M. (Chiba Univ., JAPAN) : The abstract of the 2002 Annual Meeting of the
Japan Society for Bioscience, Biotechnology and Agrochemistry
(b) Effectiveness of Biobran MGN-3 against Tumor cell Growth
The direct effect of Biobran MGN-3 on skin cancer cell growth and cytokine
production has been evaluated. Incubation of a squamous cell carcinoma [SCC13] cell
line with Biobran MGN-3 arrested tumor cell growth (30% decrease in cell number
after 48 hours and 50% at 72 hours of culture) as compared to control SCC13 cells
grown in a MEM media alone, which continued to increase in cell number.
Employing flow cytometry procedures, analyses showed that after 16 hours of
treatment of SCC13 cells with Biobran MGN-3, there was a five-fold increase in
intracellular levels of interleukin 10 [ IL-10], but no apparent change in content
of interferon-γ [INF-γ]. ELISA analyses showed 8-fold higher levels of IL-10 and a
3-fold increase in IL-12 in the culture media of SCC13 cells. However, little change
in INF-γ concentration was detected. The effect of Biobran MGN-3 on other cell
lines, such as normal and tumor breast cells and prostate cancer cells, was also
evaluated.
These findings indicate that Biobran MGN-3 acts by not only enhancing the host
immune function but also through a direct alteration of tumor cell growth and
production of cytokines. These findings may offer a mechanism of action which could
explain the high clinical success and impressive benefits of Biobran MGN-3 treatment
observed by the author over a period of 4 years.
Ghoneum M. (Drew Univ., USA) : The abstract of the 8th International Congress on
Anti-Aging & Biomedical Technolgies Conference Proceedings Manual, 2000
3.4. Complementary Effect in Cancer Therapy
(a) Evaluation of NK cell Activity and survival rates in multi-immuno therapies for
various cancer patients
A study has been reported which was designed to determine whether or not the
administration of Biobran MGN-3 could have an apothanasia effect and improve the
Quality of Life (QOL) for 205 progressive and partially metastasized cancer patients
in stages late III-IV, after surgery. Participants in the clinical study were
hospitalized patients in the Sano Surgical Clinic, Japan. They were treated with
complementary alternative medicines and conventional anticancer medicines with low
side effects.
The 205 patients hospitalized for 6 months were grouped into two groups, viz. 109
patients (control group) treated with the clinic's standard complementary
alternative medicines, and 96 patients who were in addition given Biobran MGN-3
(Biobran MGN-3 group) for one year and a half.
All the patients were measured for natural killer activity as an indication for the
variation of immunoparameter. Simultaneously, the QOL of the patients were also
checked. The NK cell activities of the patients after surgery were low on average,
however by the administration of Biobran MGN-3, NK activity was observed to increase
and the apothanasia ratio also increased; the higher the NK activity of patient, the
higher the apothanasia ratio that was observed. (Table 2) The findings indicated
that NK activity can be used as a pathological index of progressive cancers. QOL
improvement was also observed on administration of Biobran MGN-3.
Table 2: Relation between total survival rate, NK activity and survival rates in 2
groups
| Group |
Biobran Group |
Control Group |
| Total survival rate |
52/96 (54.2%) |
19/63 (33.9%) |
NK activity category
Less than 19.9%
20%-40%
More than 40%
|
17/40 (42.5%)**
18/35 (51.4%)*
17/21 (81.0%)
|
2/16 (12.5%)
7/25 (28.0%)
10/15 (66.7%)
|
% significant to the control group **p<0.01 *p<0.05
Takahara K. (Sano Surgical Clinic, JAPAN) : The Abstract of the 3rd Annual Meeting
of the Japanese Society for Complementary & Alternative Medicine & treatment, 2000
(b) Immunomodulatory and Anti-Cancer Properties of Biobran MGN-3 in 5 Patients with
Breast Cancer
Five patients with breast cancer were given Biobran MGN-3 at 3g/day, and their NK
cell activities were measured by 4-hr 51Cr-release assay using K562 tumor cells as
targets. The Results showed:
-
Patients having a low level of basal NK activity (12.7-58.3%) at effector :
to target (E:T) ratios of 12 and 100:1, had their NK activity significantly
enhanced by Biobran MGN-3 treatment (41.8-89.5%) at the same E:T ratios.
-
The augmentation in NK activity was detected as early as 1-2 weeks post
treatment and was further increased with continuation of administering
Biobran MGN-3.
-
Two patients who participated early in the study (6-8 months) went into
complete remission.
Ghoneum M. (Drew Univ., USA) : The abstract of An American Association for Cancer
Research Special Conference, 1995
(c) NK immunomodulatory function in 27 cancer patients by Biobran MGN-3, a modified
arabinoxylan from rice bran
A case in which a favourable outcome was obtained as a result of using Biobran MGN-3
as a supplement in treatment of a lung cancer which had spread from the lungs to a
wide area of bones is presented in this report.
The patient was a 67 year old male. In August, 1996, he had consulted a doctor
because of a drastic decrease in body weight and complained of severe coughing and
expectoration. The diagnosis was a complication of lung cancer (squamous cell
carcinoma) and tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis). After preferentially treating the
tuberculosis with antibiotics, treatment of the lung cancer by irradiation was
initiated in October in parallel with the tuberculosis treatment. In December of the
same year, the lower half of his right lung was excised, removing the tumor. After
irradiation treatment, he left hospital in January, 1997.
In June of the same year, he consulted the doctor again, complaining of pain in the
right breast. After diagnosis by bone scintigram, multiple osteo-metastasis was
confirmed. The tumor had spread mainly to the ribs of the right chest, but there was
also a wide dispersion to the bones of the entire body. From July, sustained-release
morphine morphine was administered as analgesic. Meanwhile, administration of
Biobran MGN-3 was started at 3g per day from the end of May. From January, 1998, his
pain decreased. While Biobran MGN-3 was continually administered, the slow-release
morphine was gradually reduced and in June, the morphine was stopped altogether. The
tumor marker ICPP was 16.8ng/ml when the recurrence was confirmed and gradually
reduced to 7.6ng/ml in December 1997 and 6.7ng/ml in June 1998. A remarkable
improvement was shown in the bone scintigram and an obvious retraction of the tumor
spread to the bones was confirmed. NK cell activity was as low as 9.0% when the
disease recurred but it gradually increased and is now maintained at a high level.
Sobajima T. (Hoshigaoka Kosei Nenkin Hospital, JAPAN) : The Abstract of the 2nd
Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society for Complementary & Alternative Medicine &
Treatment, 1999
(e) Applications of Biobran MGN-3 in Post Conventional Therapy
The concept of Tumor Dormancy therapy is becoming a major concept of cancer therapy
in Japan. The basic therapeutic policy is to prolong the patient's life while
maintaining a high quality of life. Dr Tunekawa performs the therapy when this is
the patient's wish and he regards improvement of quality of life an important
therapeutic objective. He reported that he has thirty-four cancer patients receiving
a combination of dormant chemotherapy and complementary and alternative medicine
(CAM), and described the therapeutic course for three of these:
-
Patients (primary disease): Gastric cancer in 3, pulmonary cancer in 3,
malignant lymphoma in 2, colon (rectal) cancer in 6, breast cancer in 3 and
others in 17
-
Treatment period: 6-18 months
-
Case studies
-
T.S. (60), F, gastric cancer (stage IV), cancerous peritonitis: The patient
was operated on for scirrhous gastric cancer in January 2000. In February
2000, she developed cancerous peritonitis and underwent gastrectomy at stage
IV. CA19-9 was 108. In August 2000, she visited our clinic with complaints
of abdominal pain, constipation, anemia and anorexia. CA19-9 was 390 and NK
activity was 25.6. She received a combination of TS1 and holistic therapy.
Biobran MGN-3 3 g/day was given for immune enhancement. She responded 1
month later with CA19-9 being 63. She showed a steady decrease in tumor
markers and increase in NK activity. In August 2001, 11 months later, CA19-9
became 25 and NK activity was 51.5. Almost no subjective symptoms persist
and she is now well nourished.
-
F.A. (46), F, breast cancer, metastases to the lumbar vertebra and uterine
body: The patient was operated on for breast cancer in July 1998 and was
treated with hormones and anticancer agents. She was found to have
metastases of the lumbar vertebra in March 2001 and uterine body in April
2001, and underwent hysterectomy in May 2001. She was discharged home on
Taxol and Paraplatin. In July 2001, she visited Dr. Tunekawa with a
complaint of bone pain. At that time, CA was 153, NCC-ST was 439 and NK
activity was 9.3. Paraplatin was continued and holistic therapy was started.
Biobran MGN-3 3 g/day was given for immune enhancement. Two months later, CA
became 18, NCC-ST was 28.9, NK activity was 22.0 and pain was resolved.
Subsequently, she showed a steady decrease in tumor markers and increase in
NK activity. In July 2002, CA was 14, NCC-ST was 3.2, NK activity was 59,
there was no pain and bone scintigraphic findings were less remarkable. Now
she is well nourished and is enjoying playing the drums.
Tunekawa H. (Tokai Society for Promotion of Holistic Medicine, JAPAN): Abstract from
Biobran Workshop in Berlin, 2002
(f) Assessment of Biobran MGN-3 in Treatment of Progressive Cancer
Dr Mizukami has experience of giving Biobran MGN-3 to 97 advanced cancer patients.
The kinds of cancer were stomach cancer, large intestine cancer, breast cancer, lung
cancer, pancreatic cancer, liver cancer, bile duct cancer, pharyngeal cancer,
ovarian cancer, glandulae cervicales uterine cancer, corpus uterine cancer, renal
cancer, thyroid cancer, prostatic cancer, cancer of the oral cavity, multiple
myeloma, etc. Although the patients had already received operations, chemotherapy,
radiotherapy, etc. in large hospitals, the progress of most patients was poor. They
had suffered metastasis and recurrences, and requested immunotherapy and visited Dr
Mizukami's hospital. In almost all examples of Biobran MGN-3 use, neither
chemotherapy nor radiation were used at the same time. Clinical observation and
inquiry were carried out in detail regarding the Quality of Life (QOL) of patients
taking Biobran MGN-3. Note was taken of phenomena common to patients taking Biobran
MGN-3.
There were some cases in which the QOL clearly improved after taking Biobran MGN-3.
Generally, although the QOL of advanced cancer patients tends to fall in a straight
line with progress of time, patients taking Biobran MGN-3 showed this tendency to a
reduced extent, and had a tendency to live longer with good QOL. Examples of
long-term survival were also seen.
The following concrete observations were made concerning QOL:
-
Although control of sharp pain is not easy and morphine is used in many
cases for advanced cancer patients, some of those who took Biobran MGN-3 did
not need to use morphine. Even when morphine was used, a tendency to use
smaller quantities of morphine was observed.
-
Overall a decreased tendency to feel languid was observed.
-
A decreased tendency for loss of appetite was observed.
-
A tendency to be able to stay at home and to feel good just before death was
observed.
-
Retention of clear consciousness even just before death, and a tendency to
be able to talk to their family was observed.
Dr Mizukami concluded that for advanced cancer patients, the fact that QOL does not
decrease so readily when Biobran MGN-3 is taken, is important for future cancer
medical treatment.
Mizukami O. (Health Promotion Research Institute New Life Layman Foundation, JAPAN)
: Abstract from Biobran Workshop in Berlin, 2002
3.5. Effect of Apoptosis
Biobran MGN-3 sensitizes Human T cell leukemia cells to Death Receptor (C95)-induced
Apoptosis
In this study, the effect of Biobran MGN-3 on death receptor-induced apoptosis in
human leukemic HUT 78 cell line was investigated. HUT 78 cells were pretreated with
Biobran MGN-3 and then were incubated with agonistic antibody against death receptor
(Fas, CD95). Apoptosis was determined by propidium iodide technique using FACScan.
Activation of caspase 3, caspase 8 and caspase 9 was determined by flow cytometry.
Mitochonodrial membrane potential was measured with DIOC6 dye using FACScan.
Expression of CD95 and BCl-2 were measured by flow cytometry.
Biobran MGN-3 was found to enhance anti-CD95 –induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent
manner. Increased cell death was correlated with increased depolarization of
mitochondrial membrane potential and increased activation of caspase 3, caspase 8
and caspase 9. Biobran MGN-3 treatment had no effect on the level of expression CD95
but it caused down regulation of BCl-2 expression. These results suggest that
Biobran MGN-3 increases the susceptibility of cancer to undergo apoptosis mediated
by death ligands, which may be relevant to anti-cancer activity.
Ghoneum M. (Drew Univ., USA) : Cancer Letter, 2003
3.6. Activation of Vital Defence
(a) Active oxygen radical scavenging by Biobran MGN-3
Investigations on scavenging of oxygen radicals by Biobran MGN-3 and its
fractionates have been reported. Biobran MGN-3 was fractionated into components
using a Sephadex G-25 column. Each component was named in descending order as L (L >
10,000 molecular weight), M (10,000 > M > 3,000 molecular weight), and S (3,000
molecular weight> S).
Active enzyme scavenging activity was evaluated by measuring the superoxide anion
radical (•O2) scavenging activity, hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of the
Fenton reaction (•OH), and the scavenging activity of the hydroxyl radical generated
by ultraviolet irradiation.
The results of the measurements are shown in Table. The S (low molecular weight)
fraction excelled all others in the inhibition of •OH generation caused by •O2 and
ultraviolet irradiation. High scavenging activity was observed in all fractions for
the scavenging activity of •OH generated in the Fenton reaction . (Table 3 )
Table 3
Scavenging Activity of Biobran MGN-3 on Active Oxygen radicals
(•O2 and •OH and UV induced •OH)
| Kind of Active Oxygen and SOD activity |
Scavenging ratio of Superoxide anion radical (%) |
SOD activity (U/ml) |
Scavenging ratio of UV induced Hydroxyl radical (%) |
| 20 |
2.0
(mg/ml)
|
0.2 |
20 |
2.0
(mg/ml)
|
0.2 |
20 |
2.0
(mg/ml)
|
0.2 |
BioB
BioB-L
BioB-M
BioB-S
|
64.6
39.9
49.5
90.4
|
23.0
10.4
15.6
68.1
|
4.4
0
0
26.4
|
7.6
5.0
7.2
70.5
|
0.9
0.8
1.4
15.7
|
0
0
0
2.6
|
94.9
(72.6)
97.2
(41.8)
97.0
(45.4)
96.5
(71.0
|
78.9
(35.9)
34.4
(16.5)
68.4
(9.9)
55.1
(54.9)
|
3.3
(11.5)
3.3
(1.0)
8.7
(3.9)
4.2
(19.6)
|
·O2:HPX-XOD reaction,·OH:Fenton reaction
·OH by UV light reaction:365nm,4×103J/m2/min×5
Tazawa K. (Toyama Medical and Pharmaceutical Univ., JAPAN) : Biotherapy Vol.14, 2000
(b) A basic study of arabinoxlan compound (Biobran MGN-3) on the activation of vital
defenses.
In this study, through an animal experiment, the influence of Biobran MGN-3 as
regards its biophylactic activation on survival rate in the lipopolysaccharide
(LPS)-induced lethal sepsis model was observed.
In the experiment, BALB/c mice (male, 5-7 weeks old) were used. 20mg/kg and 200
mg/kg of Biobran MGN-3 were dissolved in 0.5ml of PBS, and via an oral zonde,
administered every other day for two weeks, in total seven times. 0.5 ml of PBS was
administered orally in the same interval for the control group. 200μg/mouse of LPS
was administered intraperitoneally 12 hours after the final oral administration, and
the conditions of the mice were observed over time. In another experiment, 100
μg/mouse of LPS was administered intraperitoneally in the Biobran MGN-3 group and
control group, the mice were euthanized 0, 2, 4, 8 hr after the LPS administrations,
and peripheral blood was collected from the heart. Serum was separated, and IL-6 and
TNF were measured. IL-6 activity was measured using the B9 cell line and TNF
activity was measured by bioassay in the WEHI164-13 cell line.
As shown in Figure 9, when 200 μg/mouse of LPS was administered, the survival rate
significantly improved in groups where 20 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg of Biobran MGN-3 was
administered everyday, compared with that in the control group (20 mg/kg Biobran
MGN-3 group vs. control group, p = 0.0456; 200 mg/kg Biobran MGN-3 group vs. control
group, p = 0.0232, by Mantel-Cox test). When 100 μg/mouse of LPS was administered,
all the mice survived in groups where 20 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg of Biobran MGN-3 was
administered everyday, while 3 out of 10 mice died in the control group.
To establish the mechanism for improvement of the survival rate by Biobran MGN-3,
blood concentrations of IL-6 and TNF were measured. In the experimental group where
Biobran MGN-3 was administered, compared with the control group, the blood IL-6
level was significantly lower two hours after the administration of LPS (control
group 702.9 ± 24.7 ng/ml, Biobran MGN-3 group 403.1 ± 59.6 ng/ml; p < 0.01);
however, 8 hr after the administration, it significantly increased (control group
88.5 ± 50.0 ng/ml, Biobran MGN-3 group 441.0 ± 115.0 ng/ml; p < 0.05). Meanwhile, 4
hr after LPS administration, the blood TNF level significantly increased in the
Biobran MGN-3 group compared with those in the control group (control group 492 ±
187, Biobran MGN-3 group 1816 ± 307 pg/ml; p < 0.01).
In the LPS-induced lethal sepsis model, multiple organ failure was assumed to be
induced by a large amount of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, 6, TNF-α) released from
the reticuloendothelial system cells of the whole body, which leads to death. In
this study, significant improvement of the survival rate by the administration of
Biobran MGN-3 was observed. Possible causes were that Biobran MGN-3 intake inhibits
the production of histotoxic cytokines generated from macrophages or Biobran MGN-3
blocks the route to histotoxicity at the target cell level.
Sudo N., Kubo C. (Kyushu Univ., JAPAN) : The Japanese Journal of Clinical and
Experimental Medicine, Vol.78, 1, 2001
(c) Reduction in weight loss of mice treated with Cisplatin due to Biobran MGN-3.
In treatment of cancers platinum based drugs frequently cause substantial side
effects, such as nausea, vomiting, nephropathy and hypomagesemia due to damage of
renal tubules (Lajer & Dangaard 1999). Futhermore, in addition to hearing loss and
peripheral neuropathy, myelosuppression is one of the most devastating suppressive
side effects (Prestayko et al. 1979) leading to immunocomopromised states.
Therefore, any reducution of the side effects of cisplatin would be worthy of
achieving. To do this, the effect of Biobran MGN-3 was studied on amelioration of
weight loss of mice under tolerable maximal dose of cisplatin.
One week before cisplatin administration, Biobran MGN-3 was started to be
administered to two groups of mice at a concentration of 10mg/ml of Biobran MGN-3
(dry weight) in water or by intraperitoneal injection in a volume of 0.1 ml at the
same concentration of Biobran MGN-3 in PBS. The dose of 1 mg of Biobran MGN-3 per
mouse was calculated from that recommended for human usage (50mg/kg). One shot of
cisplatin was administered intraperitoneally in a volume of 0.1 ml at the
concentration of 15mg/kg of cisplatin in PBS containing 0.5% DMSO as a vehicle. Two
groups of mice received a gavage of water or intraperitoneal administration of PBS
and one week later cisplatin was administered to the both groups.
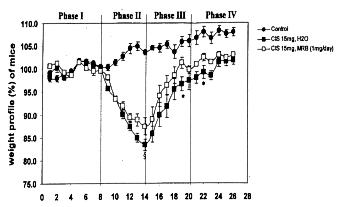
Weight loss after intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin occurred the next day in
both groups with and without administration of Biobran MGN-3. The greatest weight
loss was observed in both groups at the 5th day after cisplatin treatment, with or
without Biobran MGN-3 orally as well as intraperitoneally. The greatest weight loss
occurred in mice given cisplatin without Biobran MGN-3 administration. Although loss
of body weight in mice given Biobran MGN-3 appeared to be close to the 20% shown for
in the groups of cisplatin treatment without Biobran MGN-3, no mice died, nor did
any show diarrhea or rectal bleeding, frequent side effects of cisplatin. In the
recovery phase, earlier weight gain took place in the groups of mice given Biobran
MGN-3 than those without it.
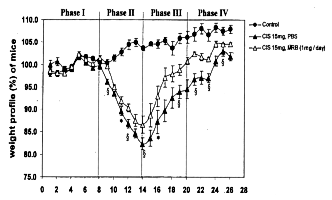
Endo Y., Kanbayashi H. (Mac Master Univ., CANADA) : Pharmacology and Toxicology,
2003
(d) The Effect of Biobran MGN-3 on Cisplatin and Adriamycin Induced Toxicity in the
Rat
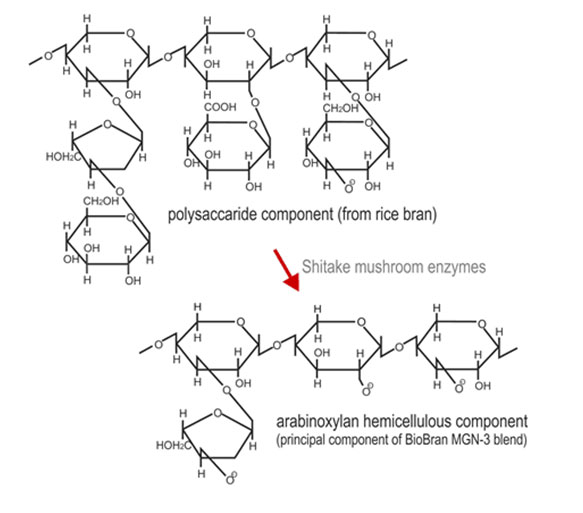
Biobran MGN-3 is derived from rice bran and is produced by the partial hydrolysis of
the water soluble hemicellulose fraction of rice bran by carbohydrases derived from
Lentius edodes mycelia [US Pat. 5560914]. Biobran MGN-3 has been shown to be a
biological response modifier producing an increase in natural killer cell activity
in immunocompromised patients [Int. J. Immunother. 14 (1) 1998].
Aim: To prevent gross pathological changes and weight loss produced
by a single dose of cisplatin (CIS) or adriamycin (ADR) by daily oral dosing of 5 or
50mg/kg Biobran MGN-3. Following an acclimation period of 13 days, male
Spraque-Dawley rats were selected for test based on body weights and assigned (10
rats/group) to each of the following (dose stated as mg/ml):
-
Biobran 5 gm PO+Veh IP
-
Biobran 50 gm PO+Veh IP
-
Biobran control PO+CIS 8mg IP
-
Biobran 5 gm PO+ CIS 8mg IP
-
Biobran 50 gm PO+ CIS 8mg IP
-
Biobran Control PO+ADR 10mg IP
-
Biobran 5 gm PO+ ADR 10mg IP
-
Biobran 50 gm PO+ ADR 10mg IP
Rats received oral (PO) Biobran MGN-3 (suspended in distilled water) or vehicle
(veh) daily for 11days. The chemotherapeutic agents or veh were administreted to
each rat by a single IP injection on Day 3. Rats were observed for clinical sings
daily for 11 days. Body weights were recorded every other day. On Day 11, all
animals were euthanized by CO2 inhalation and necropsied. Gross appearance of major
organs was evaluated and the presence of gastrointestinal damage noted.
Results: Five rats from Group 3, 3 from Group 5, and 1 from Group 4
died between D7 and 11. Rats receiving Biobran MGN-3 at 5 or 50 mg/kg PO showed a
statistically significant increase in body weight (+72%). Rats receiving CIS or ADR
alone showed a smaller increase in body weight (-1.5%, CIS; +30%, ADR). Rats
receiving Biobran MGN-3 at 5 or 50 mg plus CIS or ADR had a significantly greater
weight gain than that observed with the chemotherapeutic agent alone (Biobran MGN-3
5 mg in CIS treated rats, +11% and +46% in ADR treated rats). Biobran MGN-3 50 mg in
CIS treated rats, +44% and +43% in ADR treated rats.Surviving rats receiving Biobran
MGN-3 appeared healthier, gained weight and had a lower incidence of gross
intestinal pathology than those taking CIS or ADR without Biobran MGN-3.
Table 4: Effect of Biobran on Body Weight Loss Induced by Cisplatin
and Doxorubicin
| Treatment (all intraperitoneal) |
Day 0 |
Day 3 |
Day 5 |
Day 7 |
Day 9 |
Day 11 |
5mg/kg PO+Vehicle
50mg/kg PO+Vehicle
Control PO+Cp8mg/kg
5mg/kg PO+Cp8mg/kg
50mg/kg PO+Cp8mg/kg
Control PO+Dx10mg/kg
5mgn/kg PO+Dx10mg/kg
50mg/kg PO+Dx10mg/kg
|
100
100
103
99
101
103
101
101
|
100
98
101
99
99
100
100
101
|
100
100
82
85
92
88
92
92
|
100
97
69
76
90
82
89
87
|
100
97
55
68
85
77
86
85
|
100
97
57
65
84
76
85
83 |
PO-oral, Dx-Doxorubicin, Cp-Cisplatin
Jacoby H. I. (USA) : Journal of Nuturaceuticals, Function & Medical Foods, Vol.3 (4)
2001
(e) The effect of Biobran MGN-3 on radiation therapy induced toxicity in the mouse
This study, investigates the modifying effect of Biobran MGN-3 on radiosensitivity
as expressed in bone-marrow death caused by total body irradiation. First, with
possible clinical application in mind, the authors studied each effect
quantitatively across a wide range of radiation dosage between 4.5 Gy and 8.5 Gy.
Four or 5-week-old SPF male BALB/c mice (F2) were the subject of these experiments.
In the Biobran MGN-3 groups Biobran MGN-3 was added to the food of F2 mice at 50
mg/kg body weight. There were 10-50 mice per group. Starting at two days after
caging, the food was changed in the F2 group to Biobran MGN-3 added food. Four and
5-week-old mice were irradiated after feeding with Biobran MGN-3 for 15 days and 8
days.. Body weight was measured 3 times a week and the number of deaths was checked
every day. In some cases mice used in the experiment had been given Biobran MGN-3
for two weeks before irradiation in other cases administration of Biobran MGN-3 was
only started after irradiation.
Although in the F2 group, mortality of mice due to bone-marrow death was observed
from the seventh day after irradiation, mice tended to die a little later in the
Biobran MGN-3 groups. In the F2 group, LD50 was approximately 5.15 Gy and the dose
reduction factor (DRF) was approximately 1.14. As for body weights, a tendency
towards a heavier body weight was maintained in the Biobran MGN-3 groups. The effect
of starting Biobran MGN-3 administration earlier, suggested that it was preferable
for Biobran MGN-3 to be given prior to irradiation.
The irradiation dose of mice was calculated as being 1.21-fold of the above dosages
at their body center, meaning that LD50 in the control group was equivalent to 6.23
Gy. Though the radioprotective effect of Biobran was DRF = 1.14, which was not a
large effect, no side effects were observed in the present study.
Nakatugawa S. (Nagoya Univ., JAPAN) : The Report of Nagoya Univ., 2003
(f) Effect of Biobran MGN-3 on Experimental Liver Dysfunction in Rats
This study investigated the effect of Biobran MGN-3 on liver dysfuncution. The
effect of Biobran MGN-3 on the development of experimental liver dysfunction in rats
induced by galactosamine (GalN) and acetaminophen (AAP) was investigated. To develop
experimental liver dysfunction, GalN was administered in Experiments 1-3 and AAP in
Experiments 4 and 5.
In Experiment 1, Biobran MGN-3 of different concentrations was administered
intraperitoneally to the rats and after 1 hour GalN was administered at the rate of
800 mg/kg.
In Experiment 2, Biobran MGN-3 was administered orally, and fractionated Biobran
MGN-3 of high molecular weight and low molecular weight was administered
intraperitoneally. After 1 hour, GalN was administered at the rate of 800 mg/kg.
In Experiment 3, after being heated, hydrolysed and processed with ion exchange
resin, Biobran MGN-3 was administered intraperitoneally. After 1hour, GalN was
administered at the rate of 800 mg/kg.
In Experiment 4, Biobran MGN-3 was administered intraperitoneally or orally, and
after 1 hour, AAP was administered at the rate of 700 mg/kg.
In Experiment 5, after being heated, hydrolysed and processed with ion exchange
resin, Biobran MGN-3 was administered intraperitoneally, and after 1 hour, AAP was
administered at the rate of 500 mg/kg.
In all experiments, rats were dissected 24 hours after administration of GalN or AAP
and their serum transaminase (GOT, GPT) levels were determined.
Results
Experiment 1: In all groups where Biobran MGN-3 was administered,
the increases of serum GOT and GPT activities due to GalN-induced liver dysfunction
were significantly suppressed, compared with those in the control group. The
suppressing effect of Biobran MGN-3 on GalN-induced liver dysfunction peaked at 20
mg/kg and no further change was observed with higher concentration of Biobran MGN-3
in the suppressing effect on GalN-induced liver dysfunction.
Experiment 2: In all groups where Biobran MGN-3 or high/low
molecular weight fractions of Biobran MGN-3 was administered intraperitoneally, the
increases of serum GPT activities due to GalN-induced liver dysfunction were
significantly suppressed, compared with those in the control group. The suppressing
effects was similar to those observed with Biobran MGN-3 itself.
Experiment 3: In groups where hydrolyzed Biobran MGN-3 was
administered, the increases of serum GOT activities due to GalN-induced liver
dysfunction were significantly suppressed, compared with those in the control group.
Experiment 4: In groups of where Biobran MGN-3 was administered
intraperitoneally or orally, the increases of serum GOT activities due to
AAP-induced liver dysfunction were significantly suppressed, compared with those in
the control group.
Experiment 5: Corresponding to the results of Experiment 3, the
effect of hydrolyzed Biobran MGN-3 on AAP was assessed. In groups where hydrolyzed
Biobran MGN-3 was administered, the increase of serum GOT activities were
significantly suppressed, compared with those in the control group.
Thus, Biobran MGN-3 was confirmed to have a suppressive effect on GalN-induced or
AAP-induced liver dysfunction. The active constituent appears not to be hydrolyzed
by HCl.
Yamada T. (Chiba Univ., JAPAN): The abstract of the 6th Annual Meeting of Japanese
Association for Dietary Fiber Research, 2002
(g) Oral administration of Biobran MGN-3 alleviates common cold syndrome in elderly
people
For high-risk groups such as the elderly or children, preventive measures against
infections, such as influenza vaccination, and drastic precautions against secondary
bacterial infection are important. When community-acquired pneumonias that may have
developed through exacerbation of the common cold were investigated by age, the risk
of secondary infection by bacteria became higher in elderly people over 75 years
old. The risk of acquiring concomitant pneumonia is also high in elderly patients
with neurological disorders who are at high risk of aspiration. In the elderly whose
immunocompetence declines due to various factors, the clinical usefulness of Biobran
MGN-3 against the development of the common cold was therefore evaluated.
Elderly subjects were selected from those under the care of "Atreyu Uozaki" a health
care facility for the elderly in Kobe, Hyogo, between January and March in 2002, who
were not seriously ill, and who consented to the present study. A Biobran MGN-3
fraction (HRB) was used as the test food and rice bran containing mainly the water
soluble component, was used as the control (RB).
For the symptoms of common cold (fever, headache, fatigue, chill, cough, sputum,
nasal discharge, nasal obstruction, sore throat, chest pain), the number of days
when even a single symptom of common cold was manifest was counted. Each symptom was
converted to scores depending on its level (no symptom = "0", mild = "1", moderate =
"2", severe = "3") and the "common cold symptom score" was calculated by dividing
the accumulated score of each subject by the number of intake days.
Results: Among individual symptoms, manifestation frequencies of
"cough," "fatigue," "fever" and "sore throat" were high on starting intake of both
foods. The number of days when symptoms were manifest was fewer in the HRB group
than in the RB group. Looking at the common cold symptom score, the RB group showed
a high score in total. Although the score for "nasal symptoms" was lower in RB
group, the scores for common symptoms such as "cough," "fatigue" and "fever" were
higher. Hence it was concluded that common cold symptoms were less prevalent in the
HRB group.
This study demonstrated that when HRB was taken orally by elderly patients with the
common cold, the period of symptom manifestation was shortened, aggravation of
symptoms was halted, and the necessity for symptomatic treatment was reduced through
the extract's immunostimulatory action.
Tazawa K. (Toyama Medical and Pharmaceutical Univ., JAPAN) : Joural of Traditional
Medicines, 20 (3), 2003
3.7. Anti-Allergology Effect
(a) Evaluation of the effects of asthma prevention and symptom reduction Biobran
MGN-3 in model asthmatic mice
The effect of asthma prevention and symptom reduction by Biobran MGN-3 has been
evaluated using TDI-induced asthma model mice.
First, 2 g/litre of Biobran MGN-3 was diluted with drinking water and given daily to
the above model mice (BALB/c, female), which were divided into 4 groups (A-D) as
follows:
Group A: One month pre-administration of Biobran MGN-3 and
administration during TDI sensitization period and challenging period.
Group B: One month pre-administration of Biobran MGN-3 and
administration until the end of TDI sensitization period.
Group C: Administration of Biobran MGN-3 only during TDI
challenging period.
Group D: control group.
Group B was for the assessment of preventive effect and Group C was for the
assessment of symptom reduction effect. The effect of Biobran MGN-3 was evaluated by
blood histamine concentrations, the number of eosinophils in BALF, TDI earlobe
application test, and blood IgG1, IgG2a, IgE-type specific antibody values at
sensitization.
The peak blood histamine concentrations at 7 minutes after TDI challenge were, Group
A: 2.5±0.53, Group B: 4.2±0.75, Group C: 4.3±7.8, Group D: 6.4±0.87 (ng/ml), and
Biobran MGN-3 administration groups showed significantly lower values compared with
the control group. In the sensitization test with various concentrations (0.01-10%)
of TDI, the Biobran MGN-3 administration groups showed a reduction of sensitivity of
10-100 fold compared with the control group. In addition, the Biobran MGN-3
administration groups showed a significantly lower number of eosinophils in BALF and
lower value in TDI application test. In contrast, there were no significant
differences among blood antibody values.
In conclusion, the administration of Biobran MGN-3 showed obvious preventive and
symptom reducing effect of asthma in TDI-induced asthmatic model mice. This suggests
that Biobran MGN-3 does not affect the production of IgG1 or IgE-type antibody
induced by Th2 and that Biobran MGN-3 works as a suppressive factor against mast
cells.
Kobayashi H., Endo Y. (Mc Master Univ., CANADA) : The abstract of the 52th Annual
Meeting of Japanese Society of Allergology, 2002
(b) Inhibitory Effect of Biobran MGN-3 on the progress of Atopic Dermatitis in NC
mice
The immunoreglatory effects of Biobran MGN-3 on NC mice, which naturally develop
increased serum IgE and atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in response to
sensitisation with OVA, have been investigated. Biobran MGN-3 was given orally to
five NC mice with were compared to a control group without Biobran MGN-3. The mice
were then sensitised using OVA. Blood samples were collected biweekly before and
after the sensitisation. Amounts of total IgE, as well as OVA specific IgE, in the
sera measured by specific ELISA were significantly decreased in the Biobran MGN-3
treated NC mice compared to the control group. Furthermore, atopic dermatis-like
skin lesions was not developed in five out of five Biobran MGN-3 treated NC mice,
while all the NC mice not receiving Biobran MGN-3 developed skin lesions. It was
concluded that Biobran MGN-3 has an inhibitory effect on the progression of atopic
dermatitis in NC mice.
Nonoyama S. (Tokyo Medical and Dental Univ., JAPAN) : The abstract of the 11th
Annual Meeting of International Congress of Immunology, 2001
© Copyright 2003 by Hiroaki Maeda / Daiwa Pharmaceutical
(Thank you for permission to reprint this article on Biobran.org.)
 Glavni raziskovalec z Biobranom je bil dr. Mamdooh Ghoneum,
profesor na oddelku za imunologijo na Drew univerzi v ZDA. Dr.
Ghoneum je dandanes mednarodno priznana avtoriteta na
področju imunoterapije pri rakavih obolenjih. Svoj doktorski
naziv je pridobil na univerzi v Tokyu na temo radioimunologije.
Postdoktorski študij pa je opravil na UCLA iz imunologije. V
zadnjih 20 letih je raziskoval različne substance, ki lahko krepijo naš imunski
sistem. Zanj je Biobran MGN-3 najmočnejši imunski kompleks, ki ga je kdajkoli testiral. Biobran je pri njem pustil
tako dober vtis, da je svoje raziskave usmeril izključno na terapije z Biobranom.
Glavni raziskovalec z Biobranom je bil dr. Mamdooh Ghoneum,
profesor na oddelku za imunologijo na Drew univerzi v ZDA. Dr.
Ghoneum je dandanes mednarodno priznana avtoriteta na
področju imunoterapije pri rakavih obolenjih. Svoj doktorski
naziv je pridobil na univerzi v Tokyu na temo radioimunologije.
Postdoktorski študij pa je opravil na UCLA iz imunologije. V
zadnjih 20 letih je raziskoval različne substance, ki lahko krepijo naš imunski
sistem. Zanj je Biobran MGN-3 najmočnejši imunski kompleks, ki ga je kdajkoli testiral. Biobran je pri njem pustil
tako dober vtis, da je svoje raziskave usmeril izključno na terapije z Biobranom.



 Figure 5: Percentage of conjugate formation between natural killer
(NK) cells and K562 target cells.
Figure 5: Percentage of conjugate formation between natural killer
(NK) cells and K562 target cells.
 Figure 6: Natural killer (NK) effector-tumour targets conjugate
formation.
Figure 6: Natural killer (NK) effector-tumour targets conjugate
formation.
 Figure 7: Murine peritoneal macrophages (C3H/He mice)
Matsuura M. (Jichi Medical School, JAPAN) : Report of Jichi Medical school
Figure 7: Murine peritoneal macrophages (C3H/He mice)
Matsuura M. (Jichi Medical School, JAPAN) : Report of Jichi Medical school


